
The Global Health Expenditure Database (GHED) provides comparable data on health expenditure for more than 190 WHO Member States since 2000 with open access to the public.
Health spending indicators are key guides for monitoring the flow of resources, informing health policy development, and promoting the transparency and accountability of health systems. The database can help answer questions such as how much countries spend on health, how much of the health spending comes from government, households, and donors, and how much of the spending is channelled through compulsory and voluntary health financing arrangements. The database also includes a detailed breakdown of spending for an increasing number of countries on health care functions and primary health care, spending by diseases and conditions, spending for the under 5-year-old population, and spending by provider type.
WHO works collaboratively with Member States to update the database (Explore the Data) annually, using available information such as health accounts data, government expenditure records and official statistics. Where necessary, modifications and estimates are made to ensure the comprehensiveness and consistency of the data across countries and years. In this year's GHED update, WHO Health Accounts team published health spending in 2021. In addition, the team is also publishing the health spending data by provider type for the first time for countries with data availability.
Alongside the data, the Health Accounts team is also pleased to announce the update of individual country profiles. In the documentation center, you will find the December 2023 country release note, as well as complementary technical notes, methodology guidelines, global, regional, and country reports on health expenditure, etc.
Together with the data publication, we also released the annual report Global spending on health—Coping with the pandemic".
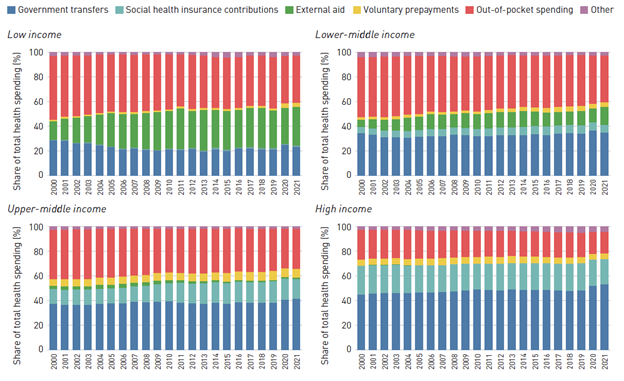
As in previous years, the report delves into the intricate landscape of global economies and health systems. This year, it focuses on health spending in 2021, providing new insights into the dynamics of increased global spending on health through the pandemic. Leveraging available detailed expenditure data from a set of countries, the report also provides insights into the strategies employed by healthcare providers to respond to new and evolving demands during the pandemic, and sheds light on how countries coped with the challenges posed by competing priorities between COVID-19 and other diseases. Additionally, the report explores health capital investments, which shape current operational capacity and are essential for forging a path toward effective and resilient health systems. Join us in gaining a deeper understanding of the complexities of global health spending through this challenging period and what it means for the future.
We renew our commitment to working closely with countries and partners to advocate the global health expenditure database as a global public good, evidence-informed policy-making processes, and promote transparency and accountability among stakeholders on the road to UHC and health security.
For any queries, please contact: nha@who.int
We renew our commitment to work closely with countries and partners to advocate the global health expenditure database as a global public good; evidence-informed policy making processes, and promote transparency and accountability among stakeholders on the road to UHC and health security.
--> The report examines the potential effects on health expenditure of the COVID-19 pandemic, given its devastating impact on health and economies across the globe. The report also features dedicated chapters on lower income countries and disease/programme expenditure. The former examines health spending patterns in a subset of countries which face important macroeconomic vulnerabilities, high levels of poverty, and are lagging behind in Universal Health Coverage (UHC) indicators. In these settings, out-of-pocket spending is larger than government spending and the governments’ priority to health has been decreasing over time. The disease/programme expenditure chapter studies spending on infectious disease, NCDs, reproductive health and immunization, as well as the revenue sources for each.
Alongside this new report and data, we are also pleased to announce the update of interactive visualisations of health spending for each country. In this section, you will be able to view, download and print individual country profiles.
In the documentation center, you will find the December 2020 country release note, as well as complementary technical notes, methodology guidelines, global, regional and country reports on health expenditure, and metadata documentation.